Image compression technologies used in security camera systems are utilized when high-resolution images require significant amounts of storage space. These technologies can compress images, thus reducing the storage space required for storage and transfer.
Image compression technologies are generally divided into two categories: lossless and lossy compression.
Lossless compression is used to reduce file size while maintaining the original image quality. This method means that the compressed image is exactly equal to the original image. Therefore, lossless compression is often used for high-quality images such as photographs.
On the other hand, lossy compression sacrifices image quality to achieve smaller file sizes. In this method, certain data is discarded from the image or the data is reorganized. Therefore, lossy compression is generally used for lower-quality images such as videos.
Popular standards among image compression technologies include JPEG, MPEG, H.264, H.265, and VP9. These standards use different encoding methods for different compression ratios and file sizes.
In conclusion, image compression technologies for camera systems allow for storing and transmitting high-quality images using less storage space. The choice of which technology to use depends on the application’s requirements.
We will explain in detail the image compression technologies JPEG, MPEG, H.264, H.265, and VP9 below.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): This is the most common image compression format. It is typically used in digital photographs and is based on lossy compression. JPEG encodes color and brightness information separately and changes the file size according to compression ratios.
MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group): This is a video compression format. There are many MPEG standards, each providing different compression ratios and quality levels. While MPEG-2 is used for applications such as DVD and HDTV broadcasts, later generation MPEG standards like MPEG-4 AVC (Advanced Video Coding) and H.264 are used for video streaming.
H.264 (MPEG-4 AVC): This is a video compression standard that provides high-quality video streams and is a popular format for both mobile devices and internet video streaming. H.264 enables the transmission and decoding of compressed video at different bit rates.
H.265 (High Efficiency Video Coding – HEVC): This is the next-generation video compression format of H.264. HEVC provides smaller file sizes using higher-quality images and less bandwidth. This is particularly important for high-resolution video streaming, such as 4K and 8K videos.
VP9: This is an open-source video compression standard developed by Google. Similar to H.265, it provides high-quality video streams and enables smaller file sizes using less bandwidth. VP9 is particularly used in platforms like YouTube.
Image compression technologies can result in different levels of disk savings depending on the format and compression level used. Generally, lossy image compression formats like JPEG experience more data loss for higher compression ratios and less data loss for lower compression ratios. Therefore, low-quality JPEG files can be compressed to very small sizes, while high-quality JPEG files may result in larger file sizes.
Video compression technologies can achieve greater savings. For example, H.264 and H.265 can encode video at much higher compression ratios and provide smaller file sizes with less bandwidth usage. This is particularly important for internet-based video streaming and other high data rate applications.
In summary, the disk savings achieved by image compression technologies depend on many factors such as format, compression level, and image content. However, video compression technologies generally provide greater savings and can deliver higher quality images.
Below, we will provide detailed information about the most commonly used compression technology today.
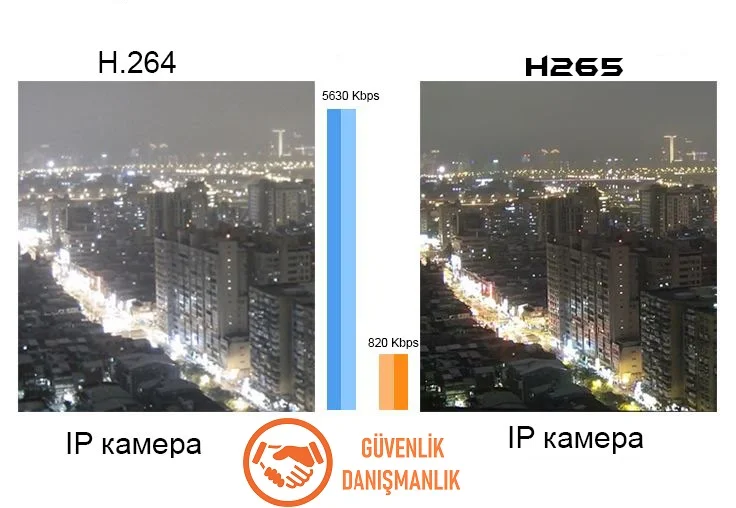
H.265, also known as High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is the next generation video compression format of H.264. H.265 provides smaller file sizes using less bandwidth while also delivering higher quality images. Therefore, it is particularly important for high-resolution video streams such as 4K and 8K videos.
By using more advanced techniques for compression ratios, H.265 can provide up to 50% better compression than H.264. This means that less bandwidth can be used for the same quality video stream.
For example, a 1-minute 4K video recording in the H.264 compression format can be 400MB in size, while the same video compressed in H.265 format can be reduced to 100MB in size. This provides advantages such as less storage space usage and faster upload/download times.
H.265, several key features including:
- Block-based motion prediction: H.265 uses block-based motion prediction to estimate the position of moving objects by comparing them with previous frames. This provides more accurate predictions compared to H.264.
- Advanced quantization: H.265 uses advanced quantization techniques to increase compression rates. This allows for higher quality images using fewer bits.
- Parallel processing: H.265 allows for parallel processing, which increases processing power and improves compression rates. This provides better performance on multi-core processors.
In conclusion, H.265 enables smaller file sizes by providing higher compression rates for high-quality video streams, using less bandwidth. This is especially important for high-resolution video streams and provides benefits such as less storage space usage and faster upload/download times.